
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/006_validate-md5-checksum-file-4037391psd-5bc0fd714cedfd00510ce242.jpg)
- #WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM HOW TO#
- #WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM CODE#
- #WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM ZIP#
- #WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM WINDOWS#
Recall though, that MD5 is known broken and should not be used for any purpose since vulnerability analysis can be really tricky, and analyzing any possible future use your code might be put to for security issues is impossible. Print hashlib.md5(file_as_bytes(open(full_path, 'rb'))).hexdigest() What is one to do about the “REMark – initialization” are those commands?, are they “set” in some other folder? what? Anyway, thanks for trying.There is a way that's pretty memory inefficient. Unix/Linx is better but overall the tech sphere does a good job repelling anyone who wants to learn a bit at a time rather than becoming a programmer. MS Help is as useful as an ice-cube in hell. I do not know that about your instructions, only that they don’t work for me. In addition many of the “suggestions” for what to enter into a terminal are not proofread and usually don’t work because of a typo -some I’ve found most I’ve wasted time with.
#WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM HOW TO#
I have used Unix terminal some and tried to use MSwhatthe f–k but always hit the same wall: the instructions assume the user already knows how to do whatever and just needs a little clarification i.e.: teckie talk to teckie. That is, you talk amongst yourselves NOT to us “uninitiated”. But I’m afraid you have made the same assumptions and/or mistakes as EVERY other teckie-trying-to-help-non-teckies that I’ve encountered over the years. Januat 10:59 C Berlin Thank you for your effort to help (at 2:31am!). REM - Not required since this is the end of the script, but there REM - If a hash method is supplied, this is used.Įcho Checking !file! against hash method !hashmethod!.įor /f "tokens=*" %%g in ('certUtil -hashfile !file! !hashmethod! ^| findstr /v "hash"') do ( REM - The success and failure messages are only displayed if hashcheck != none. REM - This check will not return anything if hashcheck = none. REM - IF NO HASH METHOD WAS PROVIDED, CHECK ALL HASHESĮcho Checking !file! against all hashes %hashes%.įor /f "tokens=*" %%g in ('certUtil -hashfile !file! %%f ^| findstr /v "hash"') do ( REM - CHECK IF PARAMETER 2 IS A HASH METHOD AND INITIALIZE REM - IF NO PARAMTERS PROVIDED OR FILE DOES NOT EXIST, DISPLAY USAGEĮcho If only the file is specified, all available hashes will be displayed.Įcho if FILE and HASH are specified, the hash will be compared to all availableĮcho hashes and a success/fail message will indicate if a match was found.Įcho This is like option 2 except that HASH is one of the available hashesĮcho and is validated against CHECK, if provided. Set hashes=MD2 MD4 MD5 SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512 Setlocal ENABLEEXTENSIONS ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION REM = If the second parameter IS NOT PROVIDED, all available hashes are REM = When done, a success/fail message is displayed. REM = a hash to verify against the file and all available hashes are used. REM = If the second parameter IS NOT an available hash method, it is used as REM = it is compared to the computed hash, and a success/fail message REM = If the second parameter matches an available hash method, it is used REM = and third are figured out contextually. The remarks at the top show how to use the script, and there is also a usage prompt if no parameter is provided or the first parameter is a file that doesn’t off
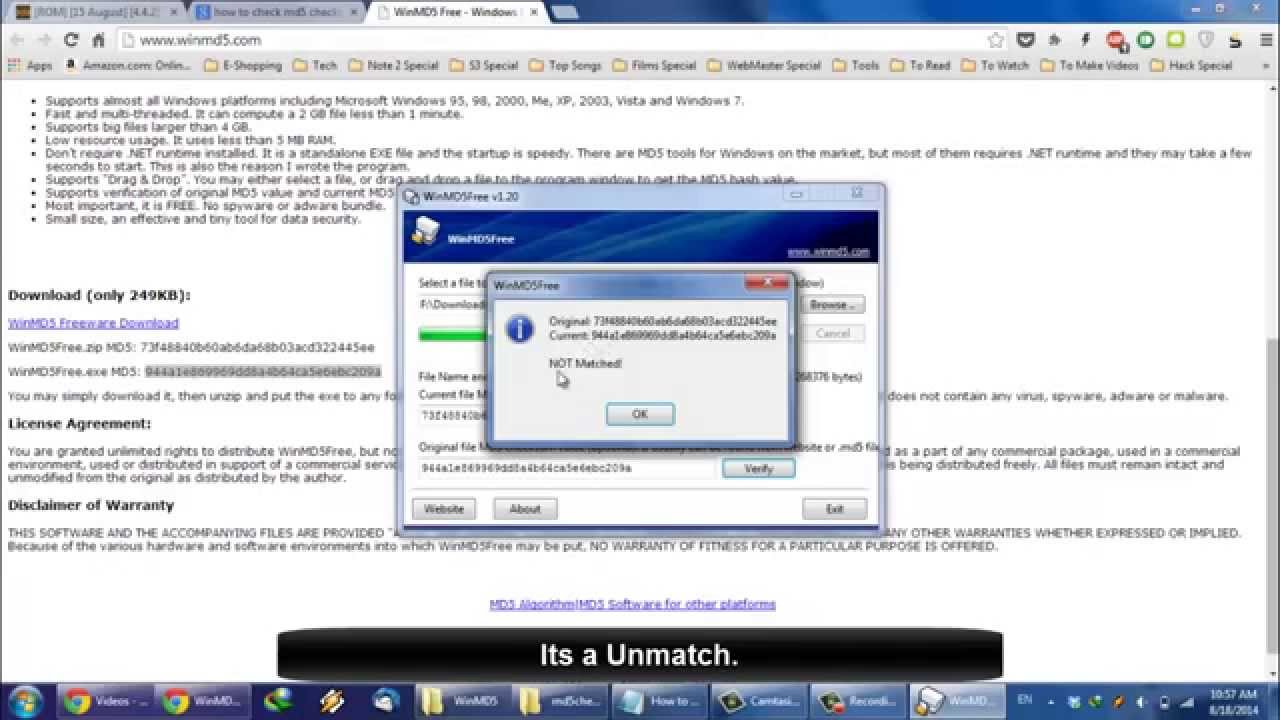
Here’s a script I wrote that takes the information in this article and shows or checks the checksum.

#WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM WINDOWS#
In the subsequent versions of Windows the case doesn’t matter. Be sure to type, for example, not “md5” but “MD5”. Hash Algorithms: Note that on Windows 7, the hash algorithms are case-sensitive. PS C:\> $(CertUtil -hashfile C:\file.img MD5) -replace " ",""Īvailable hash algorithms: MD2 MD4 MD5 SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512 SHA256 checksum example ( sha256sum): C:\> certUtil -hashfile C:\file.img SHA256Ĭ:\> CertUtil -hashfile C:\file.img MD5 | findstr /v "hash" MD5 checksum example ( md5sum): C:\> certUtil -hashfile C:\file.img MD5
#WINDOWS MD5 CHECKSUM ZIP#
In this note i will show the examples of how to make md5sum and sha256sum of a file in Windows from the command line.Ĭool Tip: zip and unzip from the command line in Windows! Read more → MD5/SHA256 CheckSum in WindowsĬhecksum a file in Windows using the built-in certUtil command-line utility: C:\> certUtil -hashfile In Windows you can make a checksum of a file without installing any additional software.įor this you can use the certUtil – built-in command-line tool that works both in Windows CMD and PowerShell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
